Search your article
Pituitary Gland
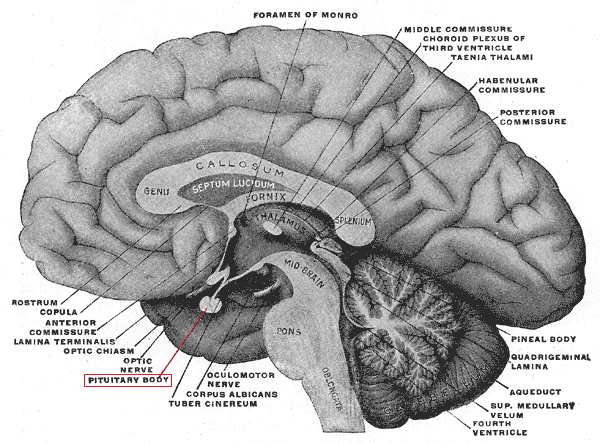
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 grams (0.018 oz) in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophysial fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity (sella turcica) covered by a dural fold (diaphragma sellae).[1]
It is regarded as the ‘master gland’ because of its role of regulating the activity of other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland secretes hormones regulating homeostasis, including trophic hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands. It is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence. [2]
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
The posterior lobe is connected to a part of the brain called the hypothalamus via the infundibulum (or stalk), giving rise to the tuberoinfundibular pathway. Hormones are made in nerve cell bodies positioned in the hypothalamus, and these hormones are then transported down the nerve cell’s axons to the posterior pituitary. Hypothalamic neurons fire such hormones, releasing them into the capillaries of the pituitary gland.[2]
The hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary are
Oxytocin comes from the paraventricular nucleus in the Hypothalamus
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH – also known as vasopressin and AVP, arginine vasopressin), comes from the supraoptic nucleus in the Hypothalamus
Anterior pituitary (Adenohypophysis)
The anterior lobe is derived from the oral ectoderm and is composed of glandular epithelium. The anterior pituitary is functionally linked to the hypothalamus via the hypothalamo hypophyseal system connection in the pituitary stalk. Through this vascular connection the hypothalamus integrates stimulatory and inhibitory central and peripheral signals to the five phenotypically distinct pituitary cell types.[2]
The hypothalamic hormones travel to the anterior lobe by way of a special capillary system, called the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system.
The control of hormones from the pituitary is in a negative feedback loop. Their release is inhibited by increasing levels of hormones from the target gland on which they act.
Intermediate lobe
There is also an intermediate lobe in many animals. For instance in fish it is believed to control physiological colour change. In adult humans it is just a thin layer of cells between the anterior and posterior pituitary, nearly indistinguishable from the anterior lobe. The intermediate lobe produces melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), although this function is often (imprecisely) attributed to the anterior pituitary.[2]
Functions
The pituitary gland helps control the following body processes:
Growth
Blood pressure
Some aspects of pregnancy and childbirth
Breast milk production
Sex organ functions in both women and men
Thyroid gland function
The conversion of food into energy (metabolism)
Occult Significance
H. P. Blavatsky described it in the following way:
The Pituitary Gland, or Hypophysis Cerebri, is a small and hard body about six lines broad, three long and three high. It is always formed of an anterior bean-shape, and a posterior and more rounded lobe, which are uniformly united. Its component parts, we are told, are almost identical with those of the Pineal Gland; yet not the slightest connection can be traced between the two. To this, however, Occultists take exception; they know that there is a connection, and this even anatomically and physically. Dissectors, on the other hand, have to deal with corpses; and, as they themselves admit, brain-matter, of all tissues and organs, collapses and changes form the soonest––in fact, a few minutes after death. When, then, the pulsating life which expanded the mass of the brain, filled all its cavities and energized all its organs, vanishes, the cerebral mass shrinks into a sort of pasty condition, and once open passages become closed. But the contraction and even interblending of parts in this process of shrinking, and the subsequent pasty state of the dead brain, do not imply that there is no connection between these two glands before death.[4]
According to Mme. Blavatsky this gland has an important role from an esoteric point of view:
There are seven cavities in the Brain . . . These cavities are called in Occultism the “Seven Harmonies,” the scale of the Divine Harmonies, and it is in these that visions must be reflected, if they are to remain in the Brain-memory. These are the parts of the Brain which receive impressions from the Heart, and enable the memory of the Heart to be impressed on the memory of the Brain.
The fourth of these cavities is the Pituitary Body, which corresponds with Manas-Antaskarana, the bridge to the Higher Intelligence; it contains various essences.[4] The seven physical Nâdîs extend up the vertebral column from the sacrum to the atlas. The superphysical are within the head, and of these the fourth is the Pituitary Body. The Pituitary Body is the organ per se of the psychic plane. Pure psychic vision is caused by the molecular motion of this body, which is directly connected with the optic nerve, and thus affects the sight, and gives rise to hallucinations. Its motion may readily cause flashes of light, seen within the head, similar to those that may be obtained on pressing the eyeballs, and so causing molecular motion in the optic nerve. When molecular action is set up in the Pituitary Body these flashes are seen, and further action gives psychic vision, as similar motion in the Pineal Gland gives Spiritual Clairvoyance. Drunkenness and fever cause disorderly motion in the Pituitary Body, and so produce illusions of sight, visions, hallucinations. This body is sometimes so affected by drunkenness that it is paralyzed, and the strict forbiddance of alcoholic liquids to all students of Occultism turns on this effect which alcohol produces on the Pituitary Body and Pineal Gland.[4]
The Pituitary Body is only the servant of the Pineal Gland, its torch-bearer, like the servants carrying torches that run before the carriage of a princess.
We begin with the mastery of that organ which is situated at the base of the brain, in the pharynx, and called by Western anatomists the Pituitary Body. In the series of the objective cranial organs, corresponding to the subjective Tattvic principles, it stands to the “Third Eye” (Pineal Gland) as Manas stands to Buddhi; the arousing and awakening of the Third Eye must be performed by that vascular organ, that insignificant little body, of which, once again, physiology knows nothing at all. The one is the Energizer of WILL, the other that of Clairvoyant Perception.[4]
When a man is in his normal condition, the introspective Adept can see the golden Aura pulsating in both the glands, a pulsation, like that of the heart, never ceasing throughout life. This motion, however, under the abnormal condition of effort to develop clairvoyant faculties, becomes intensified, and the Aura takes on a stronger vibratory and pulsating or swinging action. The arc (of the Pituitary Gland) mounts upward, more and more, toward the Pineal Gland, until finally the current striking it, just as when the electric current strikes some solid object, the dormant organ is awakened and set all aglowing with the pure Âkâúic Fire.[4]
Ajna Chakra
C. W. Leadbeater connected the pituitary gland to the ājñā chakra, the sixth center counting from below up, positioned at the eyebrow region. Although in Hinduism this chakra is traditionally considered as the “third eye”, the Theosophical view disagrees. In the latter, the third eye is identified with the pineal gland, which Leadbeater connected to the seventh chakra.[6]
He described the brow chakra as follows:
The sixth centre, the frontal (Plate IX), between the eyebrows, has the appearance of being divided into halves, one chiefly rose-coloured, though with a great deal of yellow about it, and the other predominantly a kind of purplish-blue, again closely agreeing with the colours of the special types of vitality that vivify it. Perhaps it is for this reason that this centre is mentioned in Indian books as having only two petals, though if we are to count undulations of the same character as those of the previous centres we shall find that each half is subdivided into forty-eight of these, making ninety-six in all, because its primary force has that number of radiations.[6]
Regarding its function, Leadbeater wrote:
When the sixth [chakra], between the eyebrows, becomes vivified, the man begins to see things, to have various sorts of waking visions, sometimes of places, sometimes of people. In its earlier development, when it is only just beginning to be awakened, it often means nothing more than half-seeing landscapes and clouds of colour. The full arousing of this brings about clairvoyance.
The centre between the eyebrows is connected with sight in yet another way. It is through it that the power of magnification of minute physical objects is exercised. A tiny flexible tube of etheric matter is projected from the centre of it, resembling a microscopic snake with something like an eye at the end of it. This is the special organ used in that form of clairvoyance, and the eye at the end of it can be expanded or contracted, the effect being to change the power of magnification according to the size of the object which is being examined. This is what is meant in ancient books when mention is made of the capacity to make oneself large or small at will. To examine an atom one develops an organ of vision commensurate in size with the atom. This little snake projecting from the centre of the forehead was symbolized upon the head-dress of the Pharaoh of Egypt, who as the chief priest of his country was supposed to possess this among many other occult powers.[10]
The Voice of the Silence says: “Then from the heart that power shall rise into the sixth, the middle region, the place between thine eyes, when it becomes the breath of the One-Soul, the voice which filleth all, thy Master’s voice”.[6] Commenting on this, C. W. Leadbeater said:
The special mention of the place between the eyes in our text has reference to the pineal gland and the pituitary body. The forces from both the sixth and seventh astral centres (which are between the eyebrows and on top of the head) usually converge on the pituitary body, when the etheric centre is aroused, and then vivify it and act through it. But there is a certain type of people (who are being addressed in our text) in whom the seventh astral chakra vivifies the pineal gland instead of the pituitary body, and it in that case forms a line of communication directly with the lower mental plane, without apparently passing through the astral plane in the ordinary way. Through that channel come for them the communications from within, while for the other type of people they come through the pituitary body.[6]
The Monad puts down a tiny fragment of Himself which becomes the ego . . . The very same thing happens once more when the ego repeats the operation and projects a minute portion of himself into the mental, the astral and the physical bodies of the man– a fragment which we call the personality.
This last tiny fragment is the point of consciousness which those of us who are clairvoyant can see moving about within the man. According to one system of symbology this is seen as “the golden man the size of a thumb,” who dwells in the heart; but many of us see it rather in the form of a star. I think I have always seen it myself as a brilliant star of light. A man may keep this star of consciousness where he will– that is to say, in any one of the seven principal centres of the body. Which of these is most natural to a man depends largely upon his type or Ray, and I think also upon his race and sub-race. We of the fifth sub-race of the fifth root race nearly always keep that consciousness in the brain, in the centre dependent upon the pituitary body. There are, however, men of other races to whom it comes more natural to keep it habitually in the heart, the throat or the solar plexus.[6]